반응형
문제
https://swexpertacademy.com/main/code/problem/problemDetail.do?contestProbId=AWXRDL1aeugDFAUo
SW Expert Academy
SW 프로그래밍 역량 강화에 도움이 되는 다양한 학습 컨텐츠를 확인하세요!
swexpertacademy.com
풀이
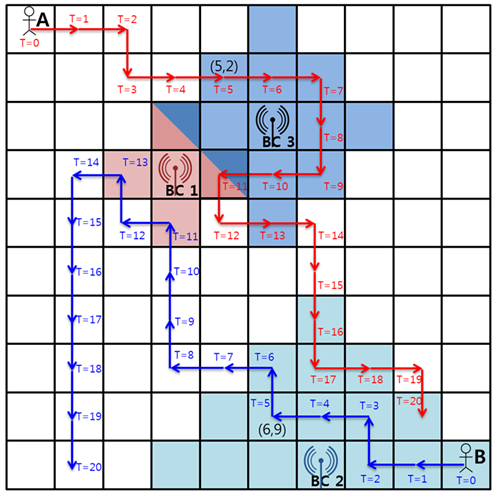
먼저 좌표 저장용 Point 클래스, BC(Battery Charger) 클래스,
A와 B의 이동정보를 저장할 배열 등을 생성하여 입력 값들을 저장하였다.
A와 B의 처음 위치를 초기화한 후 충전 가능한지 판단 후 충전하였다.
A와 B를 동시에 이동시간 1씩 주어진 방향으로 움직인 후 충전 가능한지 판단 후 충전하였다.
충전 가능한지 판단하는 할때는 A와 B의 좌표와 각 BC들의 좌표 사이의 거리를 계산 후 충전 범위 안에 있다면
각각의 list의 해당 BC의 번호(인덱스)를 저장하였다.
만약 A와 B가 접속가능한 BC들의 개수가 모두 1개 이상이라면 완전 탐색으로 가능한 조합을 모두 비교하여 처리량을 구해
최댓값인지 비교하였다.
이때 같은 BC인 경우에는 처리량을 나눠가지는 부분도 처리를 하였다.
이외에 경우 A만 BC에 접속가능하거나, B만 접속 가능한 경우
각 접속 가능한 BC들 중에 최대 처리량을 구해 결과에 누적하였다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/**
* SWEA 5644. [모의 SW 역량테스트] 무선 충전
*/
//좌표 클래스
class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 좌표 움직이는 함수
public void move(int dir) {
switch (dir) {
case 1: y--; break; // 상
case 2: x++; break; // 우
case 3: y++; break; // 하
case 4: x--; break; // 좌
}
}
}
//BC(Battery Charger) 클래스
class BC {
Point point; // 좌표
int C, P; // 충전 범위, 처리량
public BC(Point point, int C, int P) {
this.point = point;
this.C = C;
this.P = P;
}
}
public class Solution {
static int M, A, res; // 총 이동시간(M), BC 개수(A), 최대값 결과(res)
static int[] dirA, dirB; // A, B 이동정보
static BC[] BCs; // BC 배열
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = null;
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int test_case = 1; test_case <= T; test_case++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
BCs = new BC[A];
res = 0;
// A 이동정보 저장
dirA = new int[M];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
dirA[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
// B 이동정보 저장
dirB = new int[M];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
dirB[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
for (int i = 0; i < A; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// BC 정보 (x, y, c, p 저장)
BCs[i] = new BC(new Point(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()), Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())),
Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()), Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()));
}
solution();
bw.write(String.format("#%d %d\n", test_case, res));
}
bw.close();
}
private static void solution() {
// 초기 좌표 입력
Point userA = new Point(1, 1);
Point userB = new Point(10, 10);
// 처음 좌표에서 충전 가능한지 판단
charge(userA, userB);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
// A와 B 움직인후 충전 가능한지 판단
userA.move(dirA[i]);
userB.move(dirB[i]);
charge(userA, userB);
}
}
private static void charge(Point userA, Point userB) {
// A와 B 위치의 접속 가능한 BC 리스트
List<Integer> listA = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> listB = new ArrayList<>();
// BC 개수만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < A; i++) {
// A와 각 BC와의 거리가 접속 가능하다면 ( 충전범위 C >= 거리 D )
if (BCs[i].C >= (Math.abs(BCs[i].point.x - userA.x)) + Math.abs(BCs[i].point.y - userA.y)) {
listA.add(i);
}
// B와 각 BC와의 거리가 접속 가능하다면 ( 충전범위 C >= 거리 D )
if (BCs[i].C >= (Math.abs(BCs[i].point.x - userB.x)) + Math.abs(BCs[i].point.y - userB.y)) {
listB.add(i);
}
}
int max = 0, temp = 0;
// A와 B가 접속 가능한 모두 1개 이상이라면
if (listA.size() > 0 && listB.size() > 0) {
// 완전 탐색으로 가능한 조합을 모두 비교하여 최대 처리량P 구하기
for (int i : listA) {
for (int j : listB) {
temp = 0;
if (i == j) { // 같은 BC인 경우 처치량 나눠가지므로 한개만 더하기
temp = BCs[i].P;
} else { // 같은 BC가 아닌 경우 각각 처리량 더하기
temp += BCs[i].P;
temp += BCs[j].P;
}
max = Math.max(max, temp);
}
}
// A가 접속 가능한 BC가 1개 이상이라면
} else if (listA.size() > 0) {
// 접속 가능한 BC중 최대 처리량P 구하기
for (int i : listA) {
if (max < BCs[i].P)
max = BCs[i].P;
}
// B가 접속 가능한 BC가 1개 이상이라면
} else if (listB.size() > 0) {
// 접속 가능한 BC중 최대 처리량P 구하기
for (int i : listB) {
if (max < BCs[i].P)
max = BCs[i].P;
}
}
res += max; //결과 누적
}
}반응형
'Algorithm > SWEA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SWEA] 1240. 단순 2진 암호코드 (Java, 자바) (0) | 2022.02.09 |
|---|
![[SWEA] 5644. [모의 SW 역량테스트] 무선 충전 (Java, 자바)](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FcAMLPM%2Fbtru9Q7i79q%2FK8hikc9lDyhFYzZ7OrXrI0%2Fimg.png)